With the help of parameters, you can run the same workflow for different source files or time periods, parametrize expressions, and perform "what-if" analysis. Parameters can be used in action properties, in expressions, and in database queries. Parameters are also used to arrange iterations (described further in the tutorial).
A parameter has a name and a value. Anywhere where a parameter is referenced by its name, its value is used instead. Parameters allow replacing hardcoded constants or properties in workflows with values that can be easily changed by user.
Parameter Editor
Before a parameter can be used, it must be declared (created) first. Creating, editing, renaming and deleting parameters is done in the Parameter Editor. To open the Parameter Editor, select "Edit parameters" in the menu "Main", or press F6.
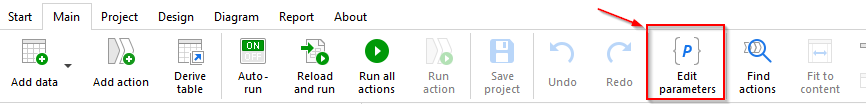
There are two types of parameters: input parameters, and calculated parameters. Input parameters are entered by a user and can be of several types. Besides general purpose parameters, there are special parameter types such as "Date" or "File path". The special parameter types have a helper button that invokes the file browser dialog or a calendar, and can be more convenient for specifying file names or dates.
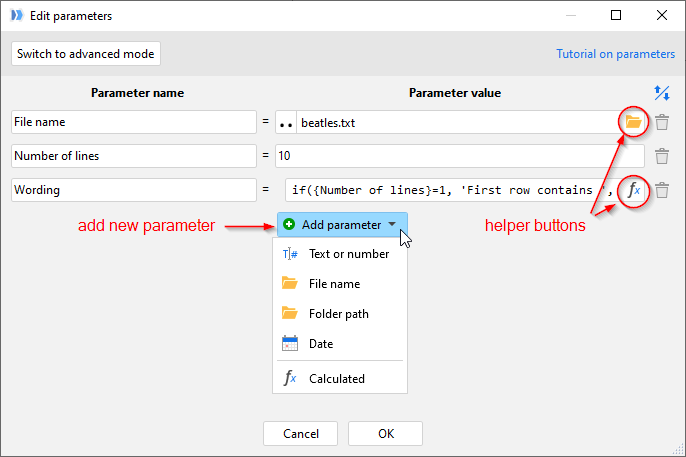
A calculated parameter is a parameter which value is calculated using an expression that can consist of arithmetical operators, functions and even other parameters. Parameter evaluation happens in a context that is outside of tables, therefore referencing a field name in a calculated parameter makes no sense and is not allowed.
Hint: A calculated parameter can refer to other calculated parameters.
The parameters of a module are accessible from all actions in the module and are constant (immutable). They do not change during project execution. A parameter has the same value for any action. Actions inside a module don't and can't change a parameter of the same module.
Using parameters in action properties
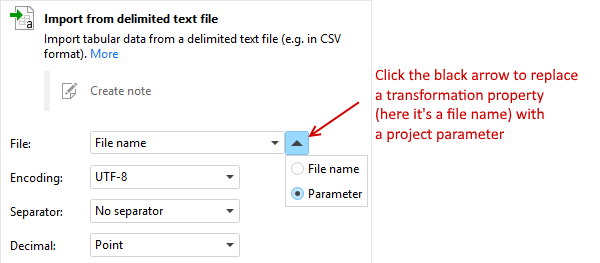
In actions, parameters can be used to specify the values of some properties. Typically, action properties such as file names, folder paths, numeric constants or dates can be specified with a parameter. Action properties that can be specified with a parameter are easy to notice — they have a black arrow next to it (see screenshot below).
Using parameters in expressions
In expressions, parameters work as constants. They can be used in arithmetic operations and functions. Parameter names in expressions should be wrapped in curly brackets. A parameter name can consist of any characters except curly brackets. For convenience, the Expression Editor has a clickable list of parameters.
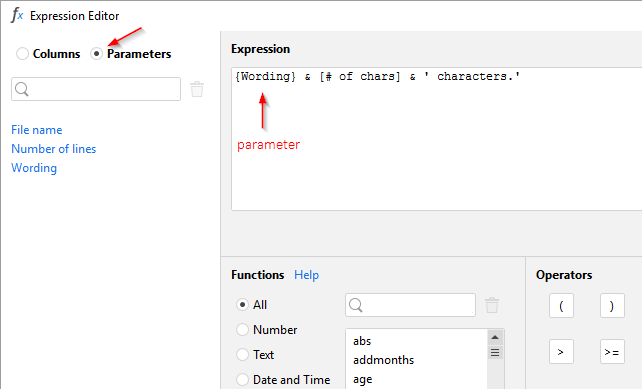
Using parameters in database queries
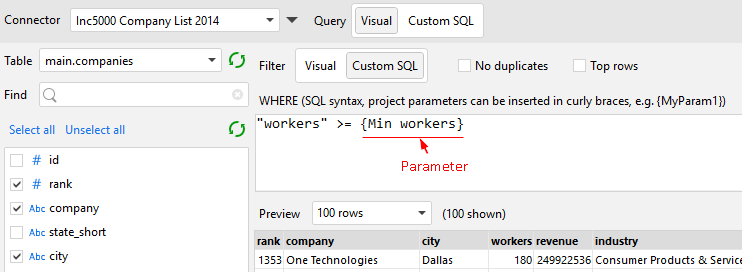
Project parameters can be used in visual database queries as well. Click the black arrow to replace a condition value with a parameter (see screenshot below).
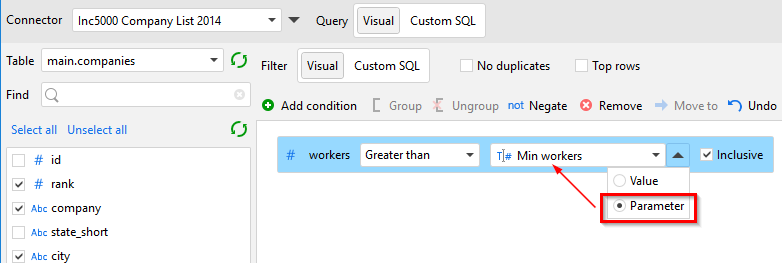
Project parameters can be inserted into a custom SQL query or WHERE clause. Before executing the query, every parameter name in curly braces is replaced with its current value (the curly braces are not inserted). Put quotes around curly braces when a text value is expected to be inserted into the query.