Understanding datasets in EasyMorph can be a bit tricky at first - especially the difference between computed and pre-computed datasets. Each has it's own pro's and con's which you must understand to choose the right one for each use case. So let's take a look at what they are, when to use each type, and specifically, how to get the most out of computed datasets.
What are datasets in EasyMorph
In short, a dataset in EasyMorph is a single table of data. However, unlike other single table formats such as a CSV file, an EasyMorph dataset can also include filters and simple charts, helping users to explore and understand the data. These additional features combine to provide what we call the “Analysis View”.
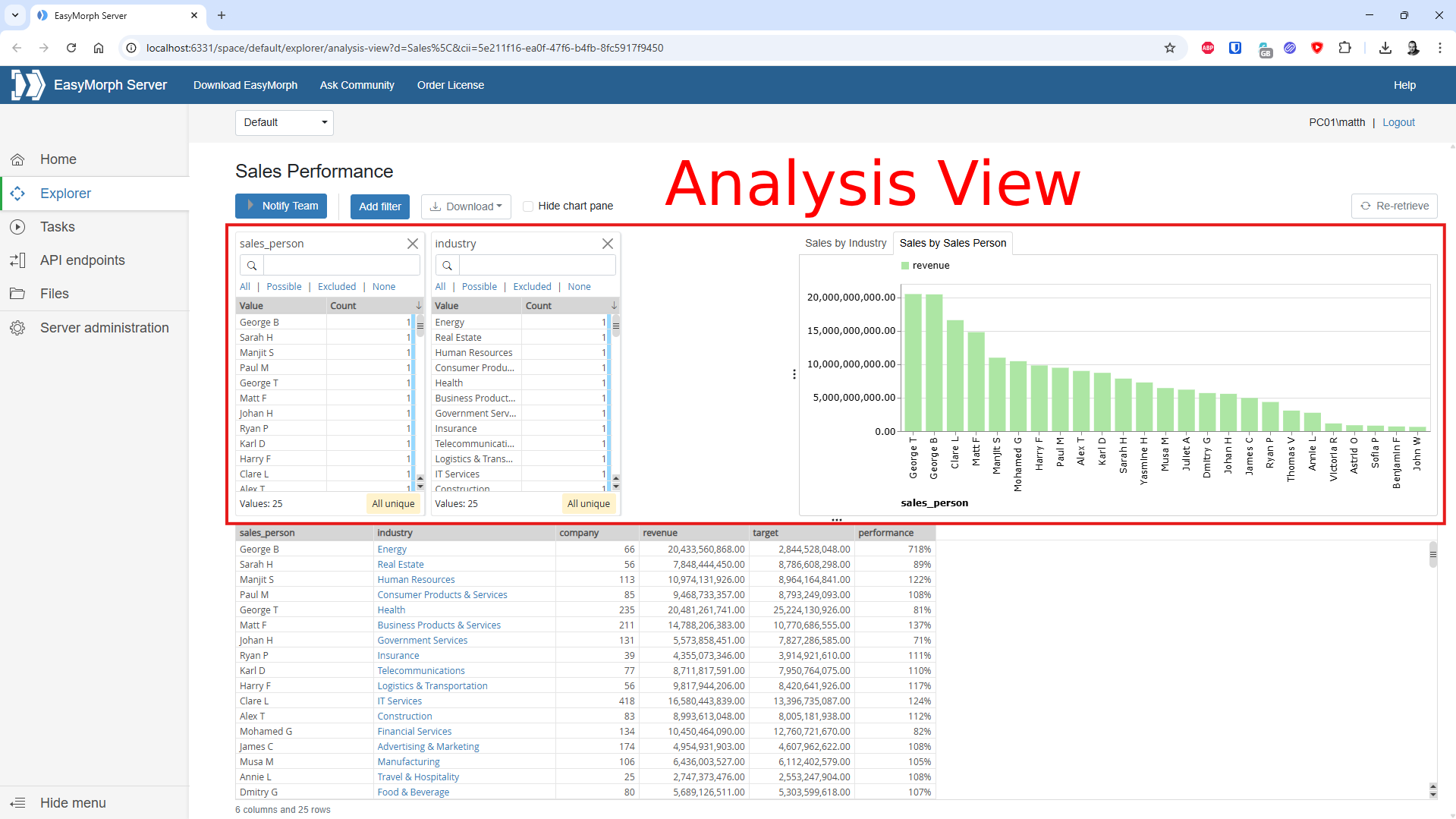
Both pre-computed and computed datasets result from running EasyMorph workflows, and so can contain data from many different sources - extracted, combined and transformed in an almost infinite number of ways.
So how do computed and pre-computed datasets differ? Although the focus of this post is computed datasets, let's first consider pre-computed datasets.
Pre-computed Datasets
Pre-computed datasets are stored by an EasyMorph workflow using the Export dataset action. When the workflow is run, the dataset is saved as a .dset file. Because they are generated in advance and saved to disk, pre-computed datasets can be accessed by users almost immediately when needed.
It’s important to note that pre-computed datasets aren’t entirely static. They can be updated by re-running the workflow which creates them. We can therefore schedule the workflow to be run at a set interval such as at midnight each day. The pre-computed dataset will therefore be updated and always contain yesterday's data.
TIP: For more information on EasyMorph .dset files, see our recent video: EasyMorph Dataset (.DSET) Files Explained.
Computed Datasets
In contrast to pre-computed datasets, computed datasets are generated on-demand when a user requests them. The relevant EasyMorph workflow is run and the resulting table of data is returned directly to the user, without it being saved as a file first. This means computed datasets always return the very latest data to the user.
However, because they are computed on the fly, if large volumes of data are returned, or if the workflow performs complex transformations steps, it may take some time for the dataset to be returned to the user.
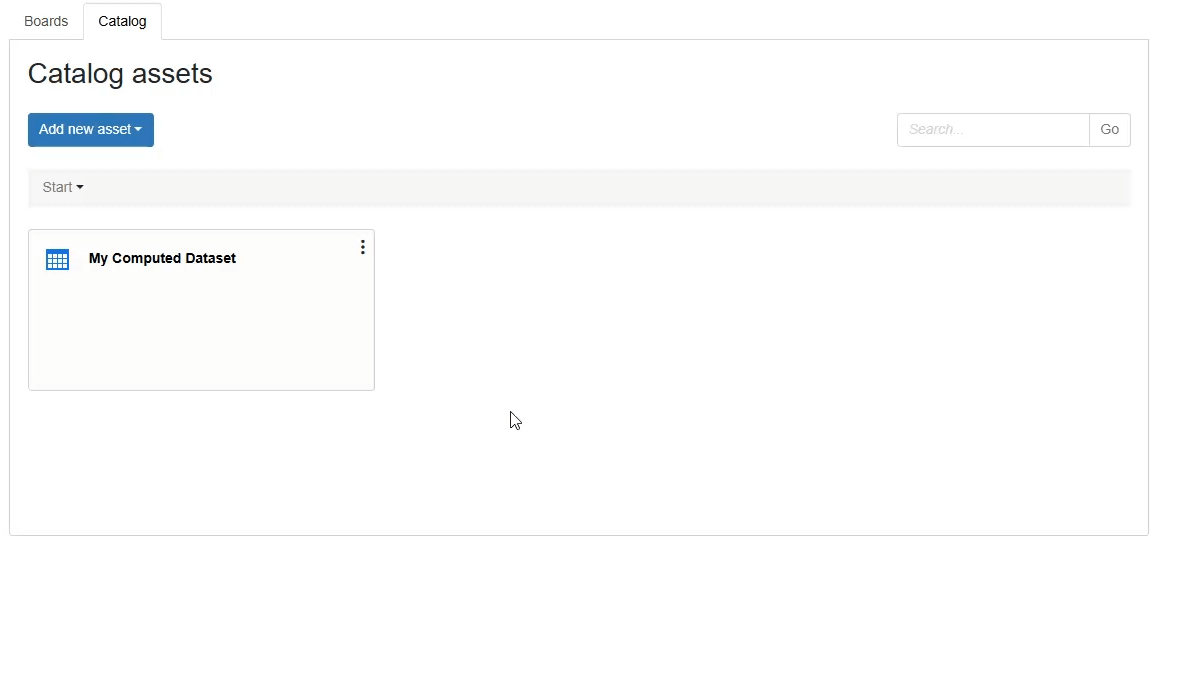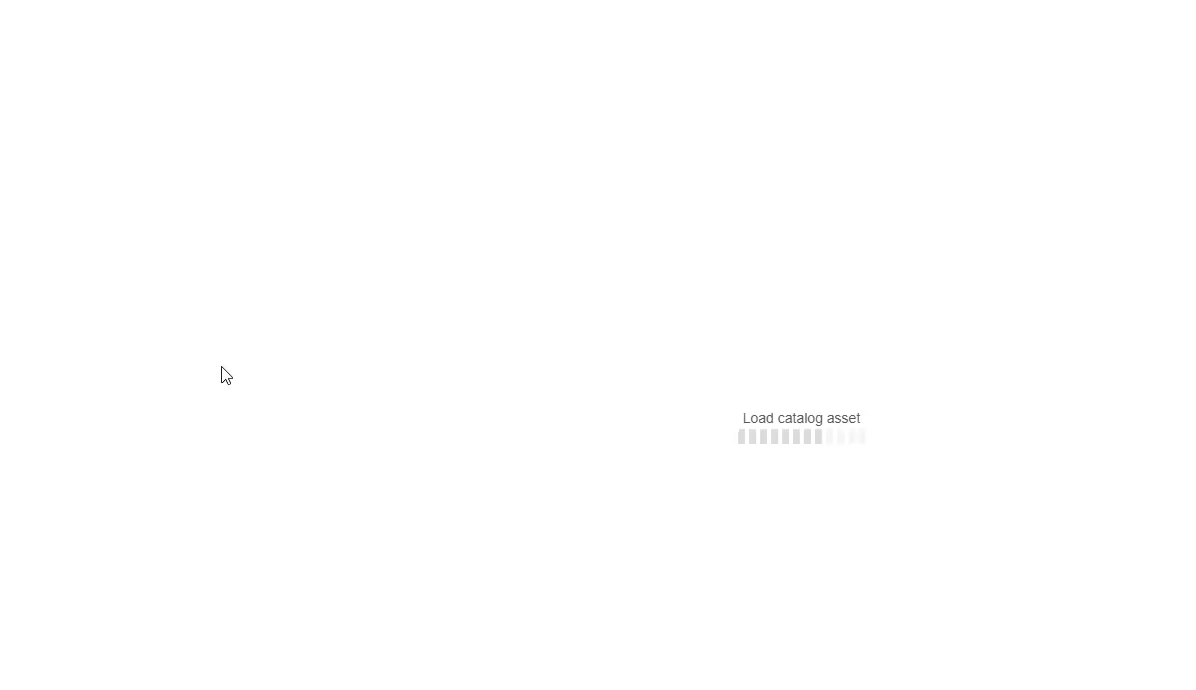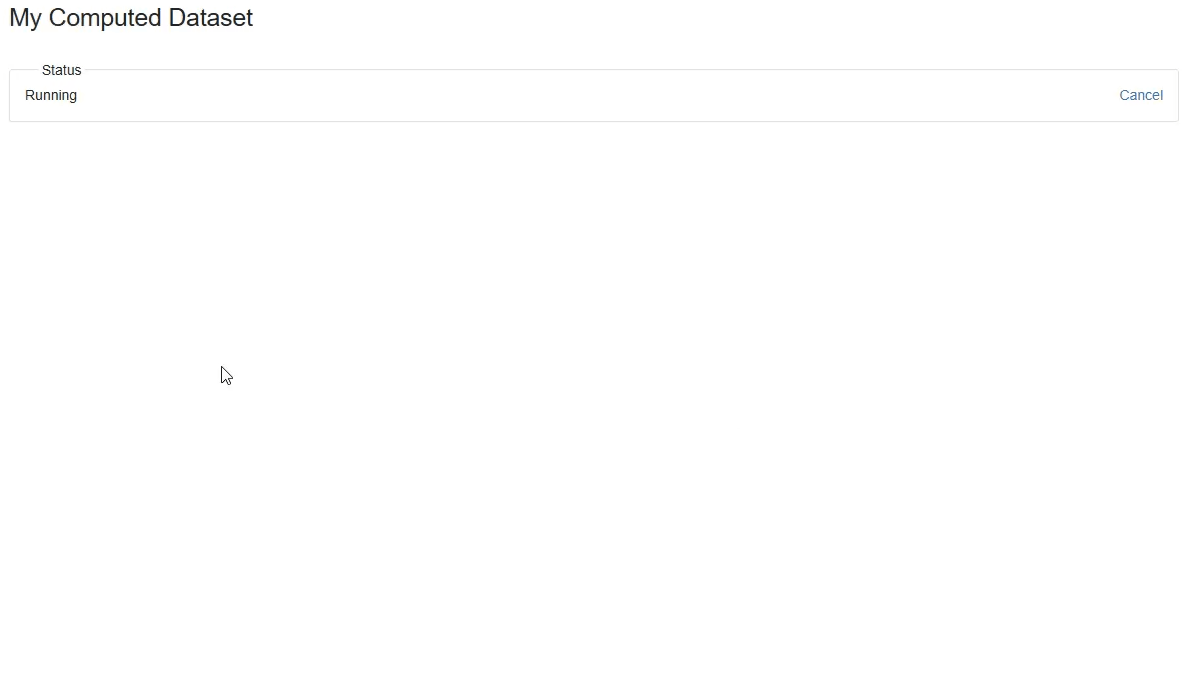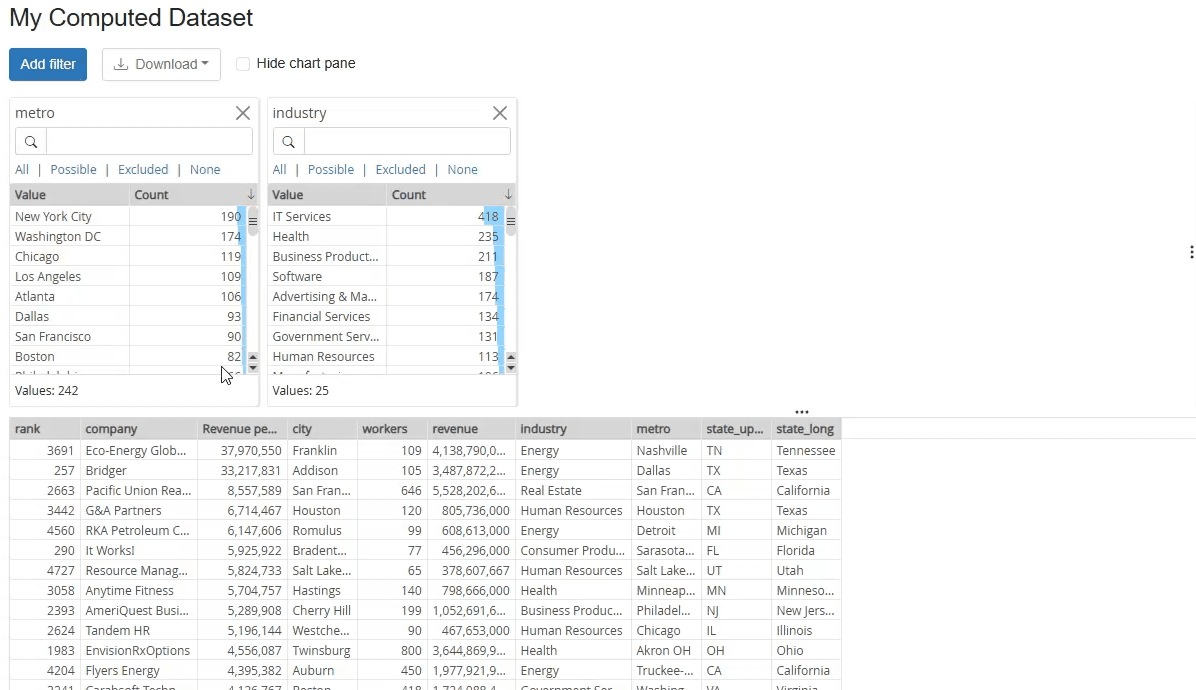
Additionally, computed datasets can be considered as a form of data virtualization. Business users can request a dataset designed to be relevant and to them, without any knowledge of which databases, files or business systems the data is stored in and how it needs to be extracted, combined and transformed. They simply request the dataset, and the underlying EasyMorph workflow takes care of the technical details.
Another big benefit of computed datasets is that they can be dynamic. EasyMorph workflows can contain parameters which can be used by the workflow in many different ways. Because a computed dataset is an EasyMorph workflow, users can enter parameter values as they request a dataset. The workflow can then used these values to define the specific dataset it returns.
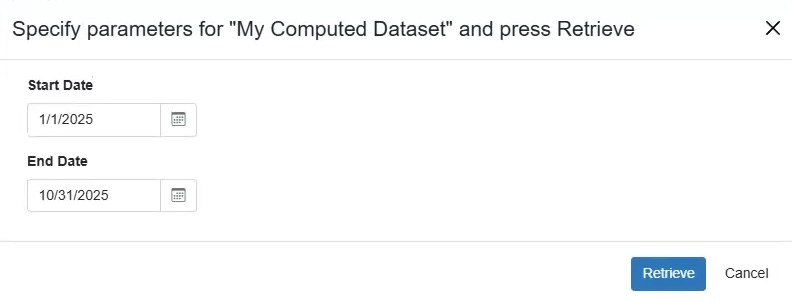
For example, a workflow could prompt the user to enter a start and end date, and then extract only data between these dates to return in the dataset. Or alternatively, accept a specific customer ID and return only orders for that customer.
Defining the Default Dataset
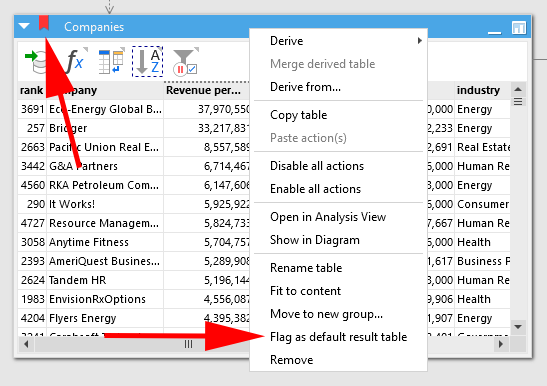
If we look at an EasyMorph workflow, we can see that it can be made up of more than one table. We therefore need to tell EasyMorph which table’s result should be returned when the workflow is used as a computed dataset.
To do so, simply right-click on the header of the table and select “Flag as default result table”. It's that easy! A red flag symbol will appear in the tables header, indicating it will be the table which is returned as the computed dataset.
Datasets and the EasyMorph Explorer Catalog
Pre-computed and computed datasets are the most common asset types added to the EasyMorph Explorer Catalog.
TIP: If you aren't familiar with the EasyMorph Explorer Catalog, I suggest watching our recent webinar on EasyMorph Explorer.
When adding a pre-computed dataset to the catalog, we select the .dset file containing the dataset, as well as giving it a name, a description, etc.

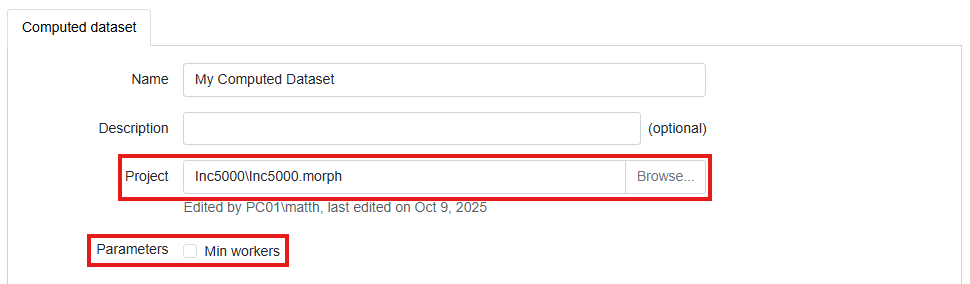
When adding a computed dataset, we instead select the EasyMorph project or .morph file which should be run to generate the dataset. We can also specify any parameters the user should be asked to enter when requesting the dataset.
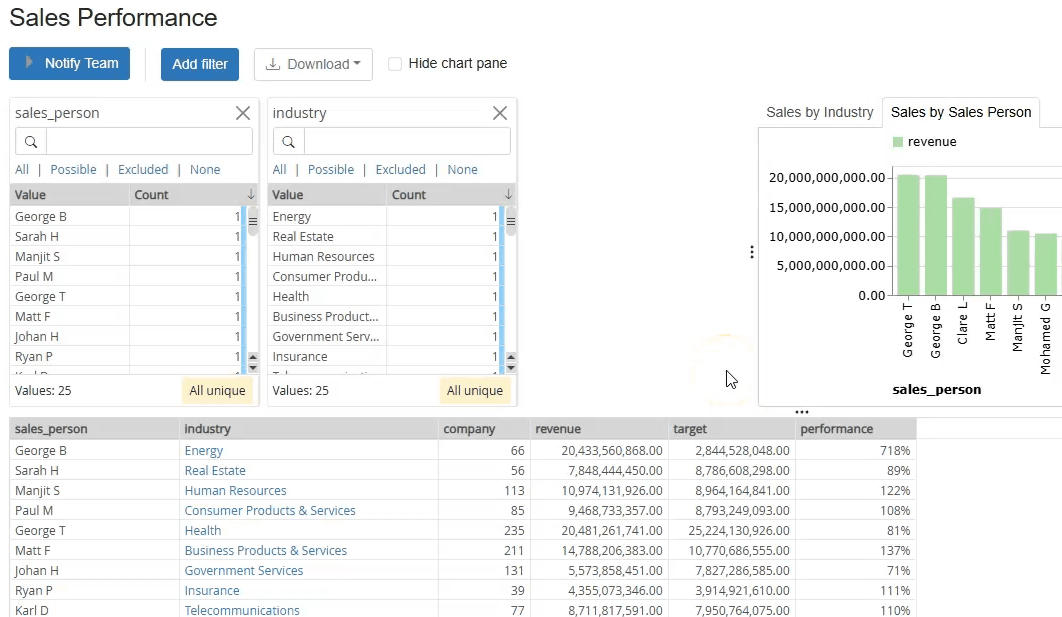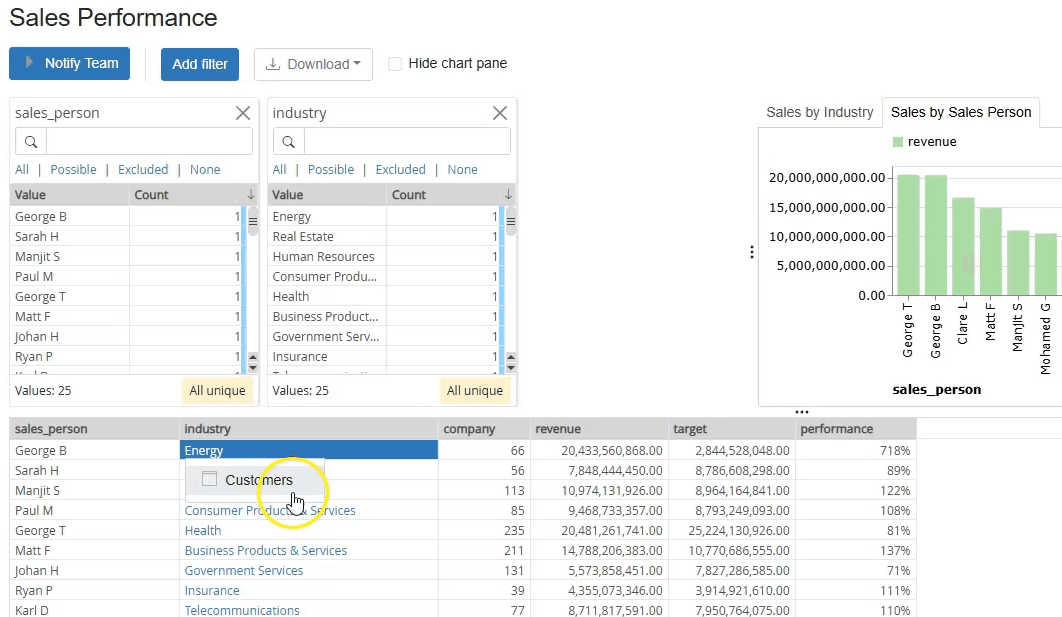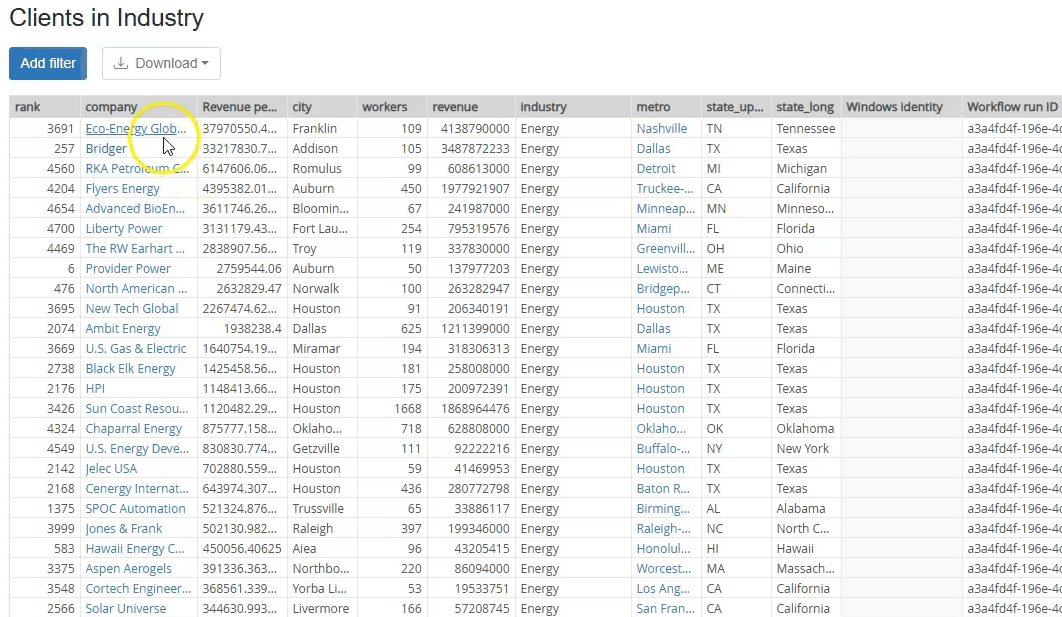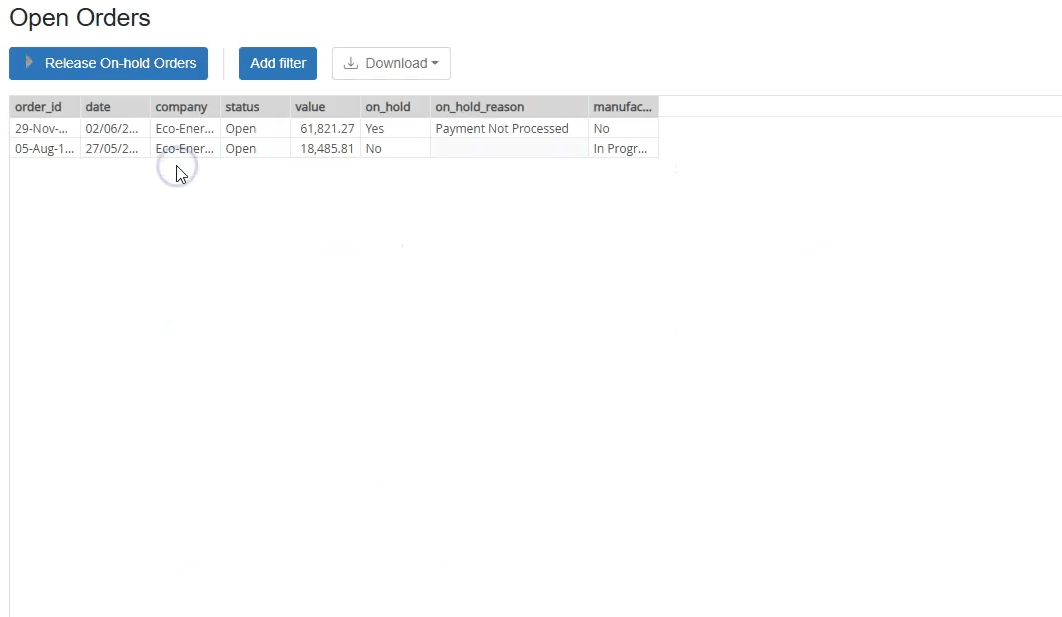
One big benefit of computed datasets and their ability to generate the table of data dynamically based on parameters, is that they can be added as commands to other datasets in the Catalog. These commands can populate the workflow’s parameters based on specific values selected by the user. For example, in the dataset below, we can see that the "Industries" are shown in blue and look like links in webpages which can be clicked. If I click on a specific industry and select the "Customers" command, it calls another calculated dataset, passing the company I clicked as a parameter, which the workflow can then use to extract a list of all customers in that specific industry.
The resulting calculated dataset can also have commands linking to other calculated datasets, allowing the user to drill into and explore the data. Calculated datasets and catalog commands therefore offer a powerful ability to interlink datasets into a rich web of data.
Summary
Both pre-computed and computed datasets can provide business information to users, when they need it, independent of which business systems it may originate from. Neither is necessarily better than the other, with each having its own pros and cons.
| Computed Datasets | Pre-computed Datasets |
|---|---|
| Based on EasyMorph workflows (.morph). | Based on EasyMorph dataset files (.dst). |
| Can contain an Analysis View. | Can contain an Analysis View. |
| Can be slow to calculate when requested, especially for large datasets or if the required workflow is very complex. | The work is done in advance so the data is immediately available when requested. |
| Can provide the very latest up-to-date data to the user. | Only as up-to-date as the last time the workflow creating it was run. Can be a benefit if you need a snapshot in time. |
| Can be dynamic, generating the data based on user input at the time the user requests it. | Will contain the same data in the same format, whoever requests it. |
Hopefully you can see the power of computed datasets and how they can be used to allow both technical and non-technical users to access the data they need, when they need it, without having to make requests to the technical teams. A huge boost to your organization's productivity is waiting to be unlocked!